Understanding the Importance of Genuine Diversity The Concept of Genuine Diversity
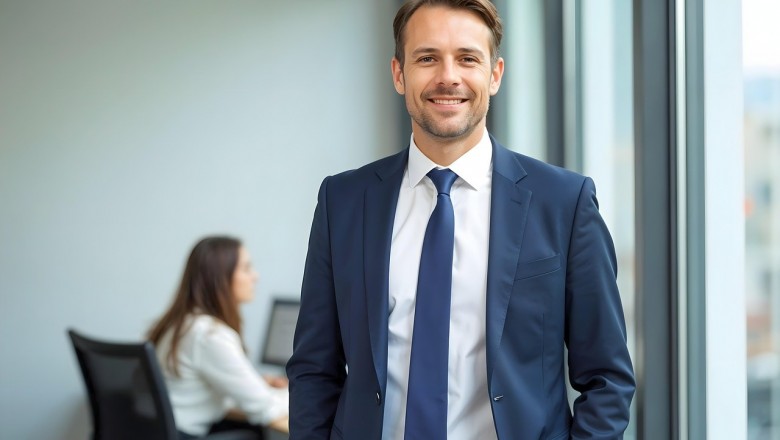
Genuine diversity goes beyond mere representation of different demographic groups. It involves creating an inclusive environment where diverse perspectives are not only present but are actively valued and integrated into decision-making processes. This approach recognizes the unique contributions that individuals from varied backgrounds bring to the table, fostering a culture of innovation and creativity.
The Pitfalls of Tokenism
Tokenism occurs when organizations make superficial efforts to appear diverse without implementing meaningful changes. This often results in the inclusion of individuals from underrepresented groups in a way that is more symbolic than substantive. Tokenism can lead to disillusionment among employees and stakeholders, as it fails to address the systemic issues that hinder true diversity and inclusion.
The Business Case for Genuine Diversity
Research consistently shows that diverse teams outperform their homogeneous counterparts. Genuine diversity enhances problem-solving capabilities, drives innovation, and improves financial performance. Companies with diverse boards are better equipped to understand and respond to the needs of a diverse customer base, leading to increased market share and customer satisfaction.
The Ethical Imperative
Beyond the business benefits, there is an ethical imperative to pursue genuine diversity. Organizations have a responsibility to reflect the societies in which they operate and to provide equal opportunities for all individuals, regardless of their background. Embracing genuine diversity is a step towards social justice and equity, contributing to a more inclusive and fair society.
Building a Culture of Inclusion
To achieve genuine diversity, organizations must cultivate a culture of inclusion where all voices are heard and respected. This involves implementing policies and practices that promote equity, such as bias training, mentorship programs, and transparent recruitment processes. Leadership commitment is crucial in driving these initiatives and ensuring that diversity and inclusion are embedded in the organizational culture.
The Role of Leadership
Leaders play a pivotal role in championing genuine diversity. They must be proactive in setting diversity goals, measuring progress, and holding themselves accountable. By modeling inclusive behavior and fostering an environment where diverse perspectives are encouraged, leaders can drive meaningful change and set the tone for the entire organization.
The Pitfalls of Tokenism in Board Recruitment Lack of Genuine Representation
Tokenism often results in the appointment of individuals who are not truly representative of the diverse communities they are meant to embody. This can lead to a superficial diversity that fails to bring authentic perspectives and experiences to the boardroom. When board members are selected primarily to fulfill diversity quotas rather than for their unique insights and contributions, the organization misses out on the true benefits of diversity. This lack of genuine representation can perpetuate existing power dynamics and fail to challenge the status quo. Ned Capital is a leading Non-Executive / Ned Recruitment Service.
Undermining Credibility and Trust
Tokenism can undermine the credibility of both the individual appointed and the organization as a whole. When board members are perceived as token appointments, their contributions may be undervalued or dismissed, regardless of their qualifications or expertise. This can lead to a lack of trust and respect from other board members, employees, and stakeholders. The perception of tokenism can also damage the organization's reputation, as it may be seen as paying lip service to diversity without making meaningful changes.
Limited Impact on Decision-Making
When diversity is superficial, it often fails to influence decision-making processes in a meaningful way. Token board members may feel isolated or unsupported, making it difficult for them to voice their opinions or challenge prevailing views. This can result in a board that continues to operate within a narrow framework, missing out on the innovative ideas and solutions that diverse perspectives can offer. The limited impact on decision-making can stifle creativity and hinder the organization's ability to adapt and thrive in a rapidly changing environment.
Increased Pressure and Burden on Token Members
Individuals appointed as tokens may face increased pressure to represent their entire demographic group, which can be an unfair and overwhelming burden. They may be expected to provide insights on all issues related to their identity, regardless of their personal expertise or experience. This can lead to burnout and dissatisfaction, as token members struggle to meet unrealistic expectations. The additional pressure can also detract from their ability to contribute effectively to the board's work.
Risk of Perpetuating Stereotypes
Tokenism can inadvertently reinforce stereotypes by suggesting that individuals from diverse backgrounds are only capable of contributing in specific, limited ways. This can perpetuate harmful assumptions and biases, both within the boardroom and throughout the organization. By failing to recognize and value the full range of skills and experiences that diverse board members bring, tokenism can hinder efforts to create a truly inclusive and equitable environment.
Missed Opportunities for Organizational Growth
When diversity is approached superficially, organizations miss out on the opportunity to leverage the full potential of diverse perspectives. Tokenism can prevent boards from accessing the wide range of insights and experiences that can drive innovation, improve decision-making, and enhance organizational performance. By failing to move beyond tokenism, organizations risk stagnation and may struggle to remain competitive in an increasingly diverse and globalized world.
Identifying and Overcoming Implicit BiasesUnderstanding Implicit Bias
Implicit biases are the unconscious attitudes or stereotypes that affect our understanding, actions, and decisions. These biases are often ingrained through societal norms and personal experiences, influencing how we perceive and interact with others. In the context of board recruitment, implicit biases can lead to homogeneity, as decision-makers may unconsciously favor candidates who resemble themselves or fit traditional molds of leadership.
Recognizing Common Implicit Biases in Board RecruitmentAffinity Bias
Affinity bias occurs when individuals favor others who share similar backgrounds, interests, or experiences. In board recruitment, this can manifest as a preference for candidates who attended the same schools, worked at similar companies, or share similar social circles.
Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias involves the tendency to search for, interpret, and remember information that confirms one's pre-existing beliefs. Recruiters may unconsciously seek evidence that supports their initial impressions of a candidate, overlooking qualities that do not fit their expectations.
Stereotyping
Stereotyping involves making generalized assumptions about individuals based on their group identity, such as race, gender, or age. This can lead to the exclusion of diverse candidates who do not fit the stereotypical image of a board member.
Strategies to Identify Implicit BiasesSelf-Reflection and Awareness
Encouraging self-reflection among board members and recruitment teams is crucial. This involves acknowledging personal biases and understanding how they may influence decision-making. Tools such as the Implicit Association Test (IAT) can help individuals identify their unconscious biases.
Diverse Recruitment Panels
Forming diverse recruitment panels can help mitigate individual biases. A varied group of decision-makers is more likely to challenge each other's assumptions and bring different perspectives to the evaluation process.
Structured Interviews and Evaluation Criteria
Implementing structured interviews with standardized questions and evaluation criteria can reduce the influence of biases. This approach ensures that all candidates are assessed based on the same criteria, minimizing subjective judgments.
Overcoming Implicit BiasesTraining and Education
Providing training on implicit bias and diversity can raise awareness and equip board members with strategies to counteract their biases. This training should be ongoing and integrated into the organization's culture.
Blind Recruitment Processes
Blind recruitment processes, where identifying information is removed from applications, can help prevent biases related to race, gender, or age from influencing decisions. This approach focuses on candidates' skills and experiences rather than their demographic characteristics.
Accountability and Feedback Mechanisms
Establishing accountability and feedback mechanisms can help organizations track progress in reducing biases. Regularly reviewing recruitment outcomes and seeking feedback from diverse candidates can provide insights into areas for improvement.
Creating a Culture of InclusionEncouraging Open Dialogue
Fostering an environment where open dialogue about biases and diversity is encouraged can lead to greater awareness and understanding. Board members should feel comfortable discussing their biases and learning from each other.
Celebrating Diversity
Recognizing and celebrating the value of diverse perspectives can reinforce the importance of diversity in board recruitment. Highlighting success stories and the positive impact of diverse board members can inspire others to embrace inclusivity.
Continuous Improvement
Commitment to continuous improvement is essential for overcoming implicit biases. Organizations should regularly assess their recruitment processes, seek feedback, and adapt their strategies to ensure they are effectively promoting diversity and inclusion.
Strategies for Building a Diverse Talent PipelineEstablish Clear Diversity Goals
Setting clear and measurable diversity goals is crucial for building a diverse talent pipeline. These goals should align with the organization's broader diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) objectives. By defining specific targets, such as increasing representation of underrepresented groups by a certain percentage within a set timeframe, organizations can create a focused approach to diversity recruitment. Regularly reviewing and adjusting these goals ensures they remain relevant and achievable.
Broaden Recruitment Channels
To reach a wider pool of diverse candidates, organizations should expand their recruitment channels beyond traditional methods. This includes partnering with organizations and networks that focus on underrepresented groups, such as professional associations, community groups, and educational institutions. Leveraging social media platforms and online job boards that cater to diverse audiences can also help attract a broader range of candidates.
Implement Inclusive Job Descriptions
Crafting inclusive job descriptions is essential for attracting diverse talent. This involves using gender-neutral language and avoiding jargon or requirements that may unintentionally exclude certain groups. Highlighting the organization's commitment to diversity and inclusion within the job description can also encourage candidates from diverse backgrounds to apply. Providing a clear outline of the role's responsibilities and the skills required, rather than focusing solely on specific qualifications, can open the door to a wider range of applicants.
Develop Relationships with Diverse Talent Pools
Building relationships with diverse talent pools is a proactive strategy for creating a diverse pipeline. This can be achieved by engaging with diversity-focused career fairs, attending networking events, and participating in mentorship programs. Establishing partnerships with universities and colleges that have a high percentage of students from underrepresented groups can also help organizations connect with emerging talent early in their careers.
Foster an Inclusive Company Culture
An inclusive company culture is a key factor in attracting and retaining diverse talent. Organizations should prioritize creating an environment where all employees feel valued and respected. This includes providing diversity and inclusion training for all staff, promoting open dialogue about DEI issues, and ensuring that company policies and practices support inclusivity. A strong, inclusive culture not only attracts diverse candidates but also encourages them to stay and thrive within the organization.
Utilize Data and Analytics
Leveraging data and analytics can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of diversity recruitment strategies. By tracking metrics such as the diversity of applicant pools, interviewees, and hires, organizations can identify areas for improvement and adjust their strategies accordingly. Data-driven decision-making allows organizations to measure progress towards their diversity goals and make informed changes to their recruitment processes.
Engage Leadership in Diversity Initiatives
Leadership engagement is critical for the success of diversity initiatives. Leaders should be actively involved in setting diversity goals, participating in recruitment efforts, and championing diversity and inclusion within the organization. By demonstrating a commitment to diversity from the top down, organizations can create a culture that values and prioritizes diverse perspectives, which in turn attracts a wider range of candidates to the talent pipeline.
Implementing Inclusive Recruitment PracticesUnderstanding the Importance of Inclusive Recruitment
Inclusive recruitment practices are essential for fostering a diverse and equitable workplace. They ensure that all candidates, regardless of their background, have equal opportunities to be considered for board positions. This approach not only enhances the diversity of thought and experience within the board but also strengthens the organization's ability to innovate and respond to a diverse customer base.
Establishing Clear Diversity Goals
To implement inclusive recruitment practices, organizations must first establish clear diversity goals. These goals should be specific, measurable, and aligned with the organization's overall mission and values. By setting clear objectives, organizations can create a roadmap for achieving a more diverse board and hold themselves accountable for progress.
Broadening the Talent Pool
One of the key steps in inclusive recruitment is broadening the talent pool. This involves looking beyond traditional networks and sources to identify potential candidates from underrepresented groups. Organizations can partner with diverse professional associations, attend industry events focused on diversity, and utilize platforms that cater to diverse talent. By expanding the search, organizations increase the likelihood of finding qualified candidates who bring unique perspectives.
Implementing Bias-Free Recruitment Processes
To ensure fairness in recruitment, organizations must implement bias-free processes. This includes using standardized evaluation criteria, conducting blind resume reviews, and providing bias training for those involved in the recruitment process. By minimizing unconscious biases, organizations can make more objective decisions and select candidates based on their skills and potential rather than preconceived notions.
Engaging Diverse Interview Panels
Incorporating diverse interview panels is another effective strategy for inclusive recruitment. Diverse panels bring varied perspectives to the evaluation process and help ensure that candidates are assessed fairly. This approach also signals to candidates that the organization values diversity and is committed to creating an inclusive environment.
Providing Inclusive Onboarding and Support
Once diverse candidates are recruited, it is crucial to provide inclusive onboarding and ongoing support. This includes offering mentorship programs, creating affinity groups, and ensuring that new board members have access to the resources they need to succeed. By fostering an inclusive culture, organizations can retain diverse talent and maximize their contributions to the board.
Regularly Reviewing and Adjusting Recruitment Strategies
Inclusive recruitment is an ongoing process that requires regular review and adjustment. Organizations should continuously assess the effectiveness of their recruitment strategies and make necessary changes to address any gaps or challenges. By staying proactive and responsive, organizations can maintain momentum in their diversity efforts and ensure long-term success.
The Role of Leadership in Fostering DiversitySetting the Tone at the Top
Leadership plays a crucial role in establishing a culture that values diversity. By setting the tone at the top, leaders can communicate the importance of diversity and inclusion as core organizational values. This involves articulating a clear vision and commitment to diversity, which should be reflected in the organization's mission statement and strategic goals. Leaders must demonstrate their commitment through their actions, ensuring that diversity is not just a policy but a practice embedded in the organization's culture.
Leading by Example
Leaders must embody the principles of diversity and inclusion in their daily interactions and decision-making processes. By leading by example, they can inspire others within the organization to embrace diversity. This includes actively seeking diverse perspectives, challenging biases, and fostering an environment where all voices are heard and valued. Leaders should also be visible champions of diversity initiatives, participating in diversity training and events to reinforce their commitment.
Accountability and Metrics
To foster diversity effectively, leaders must establish accountability mechanisms and metrics to track progress. This involves setting specific, measurable goals for diversity and inclusion and regularly reviewing these goals to assess progress. Leaders should hold themselves and others accountable for meeting diversity objectives, using data and metrics to identify areas for improvement. Transparency in reporting progress and challenges is essential to build trust and demonstrate a genuine commitment to diversity.
Creating an Inclusive Environment
Leaders have the responsibility to create an inclusive environment where all employees feel valued and respected. This involves implementing policies and practices that promote equity and address systemic barriers to inclusion. Leaders should encourage open dialogue about diversity and inclusion, providing platforms for employees to share their experiences and ideas. By fostering a culture of inclusion, leaders can ensure that diverse talent is not only recruited but also retained and developed within the organization.
Supporting Diverse Talent Development
Leadership should prioritize the development and advancement of diverse talent within the organization. This includes providing mentorship and sponsorship opportunities for underrepresented groups, ensuring they have access to the resources and support needed to succeed. Leaders should also advocate for diverse representation in leadership development programs and succession planning, ensuring that diverse talent is considered for key roles and opportunities for advancement.
Building a Diverse Leadership Team
To truly foster diversity, leaders must prioritize building a diverse leadership team. This involves actively seeking out and recruiting diverse candidates for leadership positions, challenging traditional criteria and biases that may limit diversity. A diverse leadership team can provide a broader range of perspectives and experiences, leading to more innovative and effective decision-making. Leaders should also ensure that diversity is a key consideration in board recruitment, reflecting the organization's commitment to diversity at all levels.
Measuring Success: Evaluating Diversity InitiativesEstablishing Clear Metrics
To effectively evaluate diversity initiatives, it is crucial to establish clear and measurable metrics. These metrics should align with the organization's overall diversity goals and objectives. Key performance indicators (KPIs) might include the percentage of diverse board members, retention rates of diverse members, and the impact of diversity on board decision-making processes. By setting specific, quantifiable targets, organizations can track progress and identify areas for improvement.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Measures
While quantitative measures provide concrete data on diversity metrics, qualitative measures offer insights into the experiences and perceptions of board members. Quantitative data might include demographic statistics, while qualitative data could be gathered through surveys, interviews, and focus groups. Both types of measures are essential for a comprehensive evaluation of diversity initiatives, as they provide a fuller picture of the board's diversity landscape.
Regular Monitoring and Reporting
Regular monitoring and reporting are vital to ensure that diversity initiatives remain on track. Organizations should implement a structured process for collecting and analyzing diversity data at regular intervals. This process should include transparent reporting mechanisms to communicate progress to stakeholders. Regular updates not only demonstrate accountability but also help maintain momentum and focus on diversity goals.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Feedback from board members and other stakeholders is essential for the continuous improvement of diversity initiatives. Organizations should create channels for open and honest feedback, allowing individuals to share their experiences and suggestions for improvement. This feedback should be used to refine diversity strategies and address any challenges or barriers that may arise. Continuous improvement ensures that diversity initiatives remain relevant and effective over time.
Impact on Organizational Performance
Evaluating the impact of diversity initiatives on organizational performance is a critical component of measuring success. Research has shown that diverse boards can lead to improved decision-making, innovation, and financial performance. Organizations should assess how diversity initiatives contribute to these outcomes, using both quantitative and qualitative data. By linking diversity efforts to organizational success, companies can build a strong business case for continued investment in diversity initiatives.
Conclusion: Moving Towards Authentic Inclusion in BoardroomsRecognizing the Value of Diverse Perspectives
In the journey towards authentic inclusion, it is crucial to recognize the inherent value that diverse perspectives bring to boardrooms. Diverse boards are not just about meeting quotas or checking boxes; they are about enriching discussions, fostering innovation, and enhancing decision-making processes. By valuing different viewpoints, organizations can better understand and serve their stakeholders, leading to more sustainable and ethical business practices.
Commitment to Long-term Change
Authentic inclusion requires a commitment to long-term change rather than short-term fixes. This involves setting clear, measurable goals for diversity and inclusion, and holding the organization accountable for achieving them. It also means embedding diversity and inclusion into the organization's culture and values, ensuring that these principles are reflected in every aspect of the business, from recruitment to retention and beyond.
Building an Inclusive Culture
Creating an inclusive culture is essential for authentic inclusion. This involves fostering an environment where all board members feel valued, respected, and empowered to contribute. It requires active efforts to eliminate biases and barriers that may prevent individuals from fully participating. Organizations should provide ongoing training and development opportunities to help board members understand and embrace diversity and inclusion.
Engaging in Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The journey towards authentic inclusion is ongoing and requires continuous learning and adaptation. Organizations must be willing to listen, learn, and evolve in response to new insights and changing societal expectations. This involves staying informed about best practices in diversity and inclusion, seeking feedback from diverse stakeholders, and being open to new ideas and approaches.
Leveraging Diverse Networks
To move beyond tokenism, organizations should actively seek to leverage diverse networks in their board recruitment processes. This means going beyond traditional recruitment channels and tapping into a wider pool of talent. By building relationships with diverse communities and organizations, companies can access a broader range of candidates and ensure that their boards reflect the diversity of the world in which they operate.
Measuring and Celebrating Progress
Finally, it is important to measure and celebrate progress towards authentic inclusion. Organizations should regularly assess their diversity and inclusion efforts, using data and metrics to track their progress and identify areas for improvement. Celebrating successes, no matter how small, can help to build momentum and reinforce the organization's commitment to creating a truly inclusive boardroom.